UI vs UX Understanding the difference and Why both matter
Introduction
In today’s digital world, creating a successful product isn’t just about how it works but also how it feels and looks.When developing a successful product, two crucial elements come into play:
- User Experience (UX)- Relates to how the user feels when interacting with a product or service
- User Interface (UI)- This one relates to the overall look and feel of a product from a user’s perspective
Although people often confuse these terms, they serve different but equally important functions in making a product that users enjoy.
Why is this balance so important? Consider using an app that looks stunning (good UI), but quickly becomes frustrating due to its complicated navigation or slow processes (poor UX). Alternatively, look at an app that’s simple and efficient to use (good UX) but visually unappealing can leave you feeling uninspired to use it or even return. Striking a balance between the two is key to delivering a seamless and pleasant user journey fostering loyalty and ensuring long-term success.
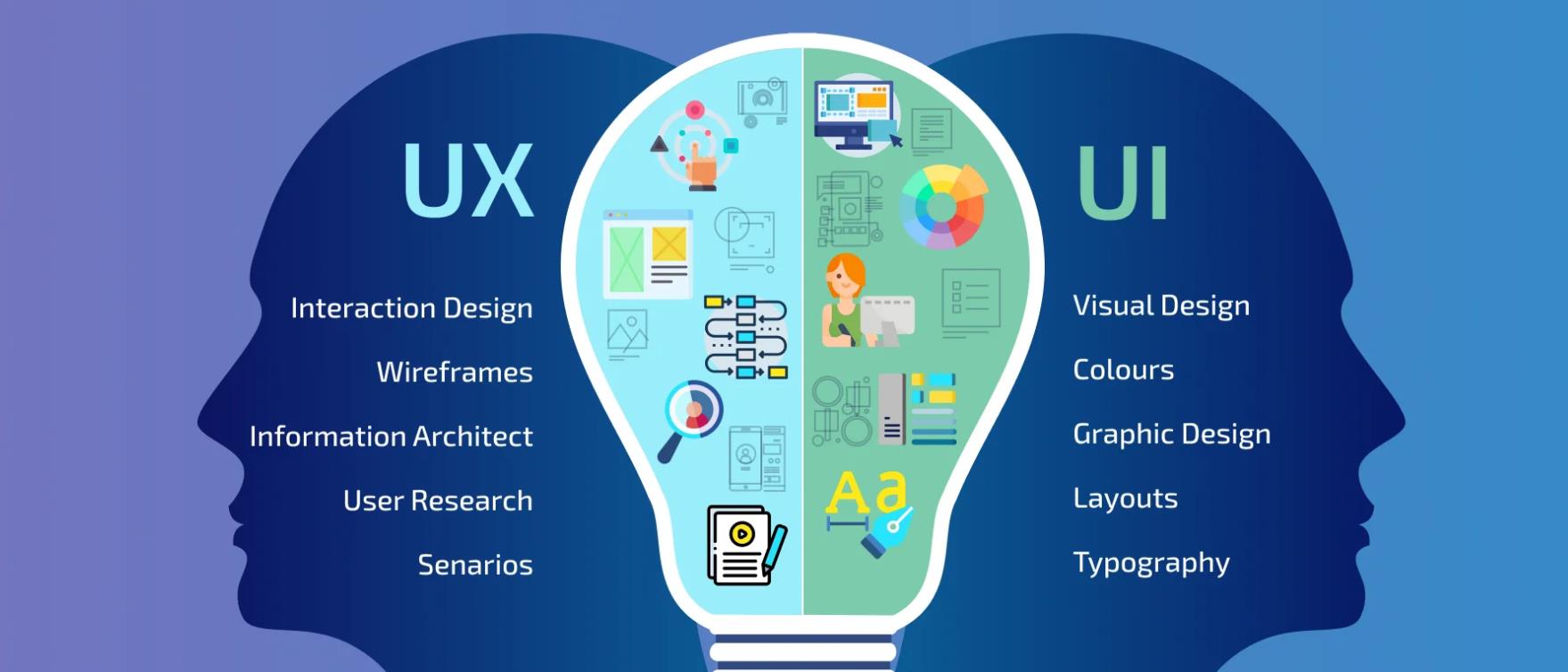
What is User Experience (UX)?
This is the overall experience a user has when interacting with your product or service. UX applies to anything that can be experienced ,be it a website, a coffee machine, or a visit to the supermarket. It encompasses every aspect of the user’s journey, from initial contact to the final outcome, shaping how they perceive and feel about the product.
A Good UX design prioritizes user satisfaction by ensuring that the interaction is intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable.
Key elements of UX include:
- User Research: Understanding the needs and preferences of the target audience.
- Usability: Creating a product that is easy to navigate and use.
- Information Architecture: Structuring content to support clear navigation and logical flow.
- Interaction Design: Designing how users interact with the product to make it engaging and seamless.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Providing users with clear responses to their actions, enhancing their understanding of the product
What is User Interface (UI)?
The user interface is the point at which human users interact with any digital device, website or application. The goal of effective UI is to make the user’s experience easy and intuitive, requiring minimum effort on the user’s part to receive the maximum desired outcome
UI design considers the look, feel, and interactivity of the product. It encompasses all the elements that users engage with, including buttons, icons, layouts, colors, typography, and overall aesthetics.
Key Elements of UI Design include:
- Visual Hierarchy: Guides users’ attention to important information through size, color, and placement.
- Color Choices: Selecting colors that match the brand’s personality and create the right mood for users.
- Typography: Enhances readability and conveys personality through the selection of fonts and text styles.
- Buttons and Controls: Clearly labeled interactive elements that enable users to perform actions easily.
- Responsiveness: Ensures the UI adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices for consistent usability.
How UX and UI Work Together
While UX and UI serve different purposes, they are inseparable when it comes to building a great product. UX lays the groundwork for a product, focusing on how it works and making sure users can navigate it effectively. UI then builds on that foundation, creating an engaging, visually appealing interface that enhances the overall experience.
Here’s how they complement each other:
- Seamless Integration: UX designs the user’s journey, and UI ensures that journey is visually smooth and aesthetically engaging.
- Shared Goals: Both UX and UI aim to create a positive user experience. UX focuses on functionality, while UI ensures the experience is enjoyable from a visual standpoint.
- User-Centered Design: UX research informs UI design decisions. Knowing the target audience helps UI designers create interfaces that resonate emotionally with users.
- Feedback Loop: UX testing helps refine UI elements, while UI prototypes help identify areas for UX improvement. This iterative process ensures continuous enhancement of both form and
The UX/UI Design Process and Tools
Creating a seamless user experience and an appealing user interface doesn’t happen overnight. It requires a strategic design process and the right tools to ensure both elements are aligned and meet user needs.
Let’s break down the common stages of this process and the tools often used:
1. Research and Discovery
The process starts with understanding the target users. This involves:
User Research: Conducting surveys, interviews, and studying user behavior to learn what the users need and expect.
Tools: Google Analytics or UserZoom to collect and analyze user data.
2. Wireframing and Prototyping
Once the research is done, the next step is to sketch out the structure of the product (wireframes) and create interactive prototypes.
Wireframing: Mapping out the flow and layout of the user interface. Prototyping: Building a mock version of the product to test interactions and user flows. Tools: Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch are popular tools for wireframing and prototyping.
3. UI Design
After the structure is set, it’s time to design the visual elements—colors, typography, buttons, and layouts—ensuring the look reflects the brand and enhances the user experience.
Tools: Adobe Illustrator, Figma, or Sketch for UI design, and sometimes even Adobe Photoshop for detailed graphics.
4. Testing and Iteration
After the designs are created, usability testing comes in. This stage involves testing the product with real users to gather feedback and identify any issues.
A/B Testing: Trying out different UI designs or interactions to see which one performs better. User Testing: Observing users as they navigate the product. Tools: UserTesting, Maze for gathering user feedback and analyzing performance.
5. Development Handoff
Once the designs are finalized and tested, they are handed off to developers who will bring them to life by coding the actual product.
Tools: Figma and Zeplin can generate code snippets and provide detailed design specifications for developers.
6. Launch and Continuous Improvement
Even after the product is launched, the process doesn’t stop. UX/UI is constantly evolving, as user behavior changes and feedback continues to pour in. Regular updates based on user feedback ensure the product remains engaging and efficient.
By following this cycle and using the right tools at each step, UX and UI designers work together to create an engaging, user-friendly product that’s visually appealing and easy to use.
Conclusion
A solid UX/UI design process, backed by thorough research, testing, and iteration, is key to building successful products that resonate with users. By focusing on both, businesses can create engaging, efficient, and delightful experiences that keep users coming back.
