Mastering CI/CD Pipelines, The Key to Rapid Software Delivery

CI/CD Pipeline: Delivering Quality Software Quickly
Delivering quality software quickly is more critical than ever in today’s software development industry. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines have become essential tools for development teams to transition code seamlessly from development to production. By enabling frequent code integrations and automated deployments, CI/CD pipelines help teams avoid the dreaded “integration hell” and ensure a consistent, reliable software release cycle.
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of CI/CD pipelines—what they are, how they work, and why they’re necessary in modern software development. We’ll delve into the various stages of a CI/CD pipeline, share real-world examples with tools like GitHub Actions, and provide strategies to optimize pipeline performance.
Additionally, we’ll discuss how to choose the right CI/CD platform for your organization, evaluating factors such as cloud-based vs. self-hosted solutions, integration capabilities, and ease of use.
So, let’s dive in.
What is a CI/CD Pipeline?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (or Deployment). At its core:
- Continuous Integration (CI) is a process where incremental code changes are frequently integrated into a shared repository. These updates are validated through automated build-and-test workflows to ensure reliability.
- Continuous Delivery (CD) automates the deployment of validated code to staging or production environments, ensuring swift and efficient rollouts.
A CI/CD pipeline combines these practices into an automated framework that moves code changes from a developer’s machine to production reliably and efficiently.
The Evolution of CI/CD
Before the advent of CI/CD, software teams often faced “integration hell”—a scenario where developers worked in isolation for extended periods, leading to time-consuming and error-prone code integration. Deployments were manual and unreliable, often requiring extended downtime and maintenance windows.
With the rise of agile methodologies and the need for faster delivery cycles, CI/CD emerged as a solution. What began as basic scripts to automate builds has evolved into sophisticated pipelines capable of delivering code changes to production multiple times a day.
Continuous Deployment
In some cases, CI/CD extends to Continuous Deployment, where code changes pushed to the repository are automatically deployed to production without manual intervention. Together, these interconnected practices form the backbone of modern software delivery, typically maintained through a DevOps or Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) approach.
Benefits of CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines offer several advantages:
- Improved collaboration: Developers and teams work more cohesively.
- Enhanced code quality: Automated testing catches issues early.
- Agility: Faster iterations and delivery cycles.
- Reliability: Reduced risks and errors during deployments.
Stages of a CI/CD Pipeline
A CI/CD pipeline typically consists of several stages, each with a specific role in the software delivery process:
- 📥 Source Stage:
- Code changes are checked out from a version control system like Git.
- 🔧 Build Stage:
- The application is compiled or built from the source code.
- ✅ Test Stage:
- Automated tests run to ensure code integrity and functionality.
- 🚀 Deploy Stage:
- The application is deployed to staging or production environments.
Additional Activities
Depending on the pipeline’s complexity, other activities may be included, such as:
- Code analysis: Tools like SonarQube ensure code quality.
- Approval gates: Human approvals for sensitive deployments.
- Environment configuration: Managing variables and secrets.
- Monitoring and alerting: Ensuring health and performance of deployed applications.
By understanding and implementing these stages effectively, teams can unlock the full potential of CI/CD pipelines for delivering quality software at speed.
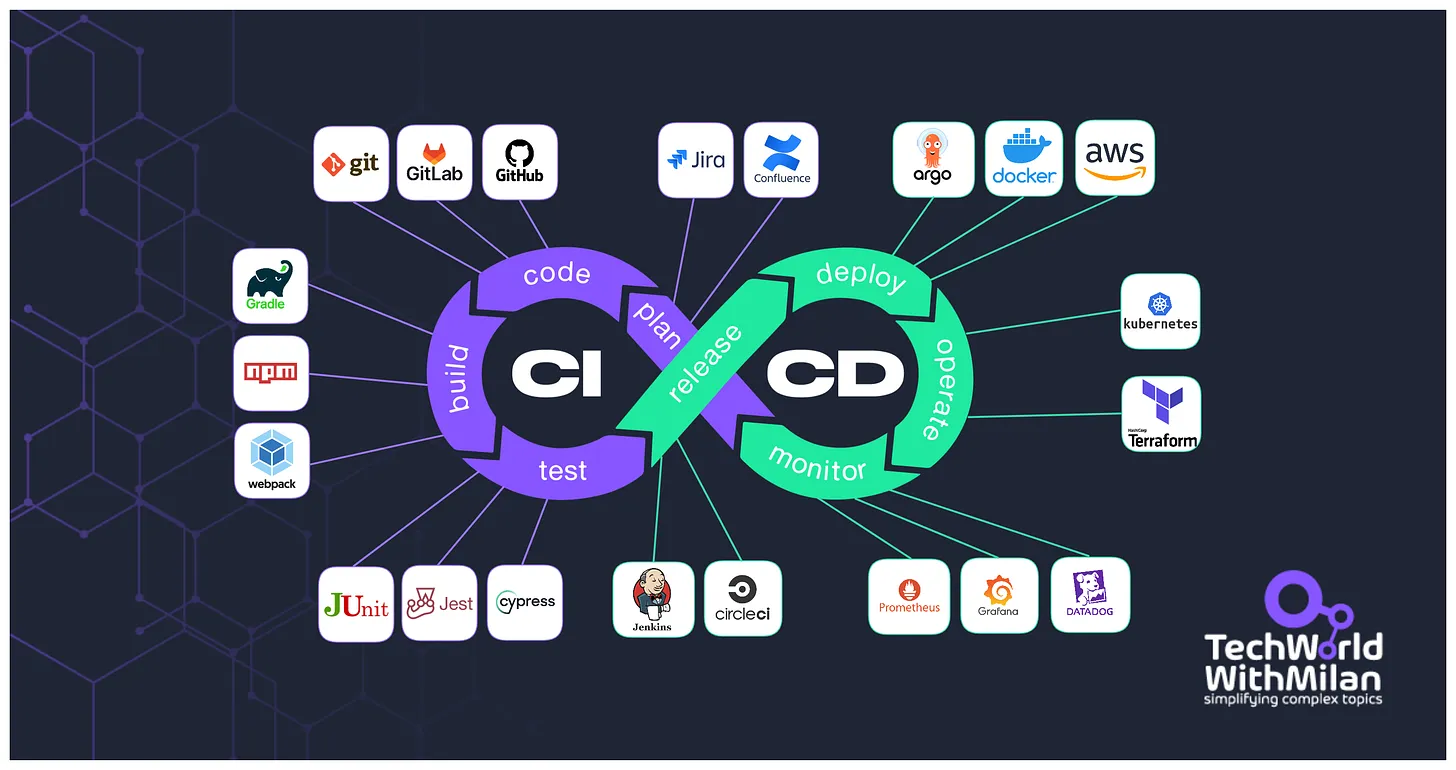
Real-Life Example of a CI/CD Pipeline
A typical CI/CD pipeline in action might look like this:
- Code Commit: A developer pushes code changes to the GitHub repository.
- Automated Build: GitHub Actions triggers a workflow to build the application.
- Automated Testing: The workflow runs unit tests and integration tests to validate code quality.
- Deployment to Staging: Upon passing tests, the application is deployed to a staging environment for further validation.
- Approval for Production: A team member reviews and approves the deployment, ensuring all checks are satisfied.
- Deployment to Production: The application is deployed to the production environment, making it available to end users.
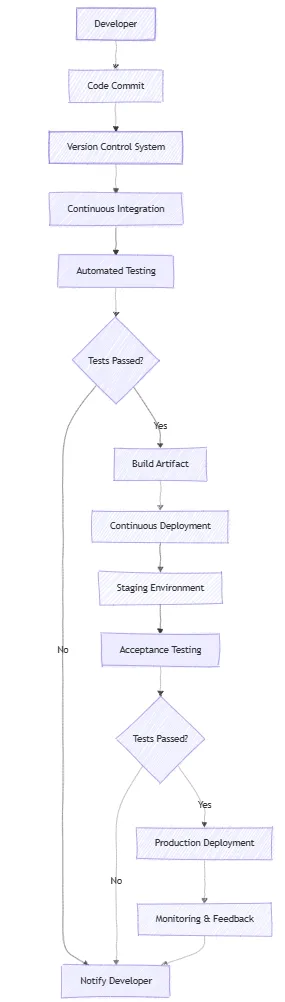
Optimizing CI/CD Pipeline
If you already have a CI/CD pipeline, here are key strategies to improve its performance, especially if the process takes a long time:
1. Identify Bottlenecks
- 🔀 Lack of parallelism: Sequential processes can slow down the pipeline. Enable parallel execution where applicable.
- ⏳ Long-running tests: Optimize or parallelize tests that take excessive time.
2. Streamline the Build Process
- 🗑️ Remove unnecessary dependencies: Eliminate unused libraries or modules to reduce build complexity.
- ⚙️ Optimize build configurations: Fine-tune build settings and infrastructure to speed up build times.
3. Improve Testing Efficiency
- 🎯 Prioritize critical tests: Run essential tests first to identify major issues early.
- 🐳 Use test containers: Isolate tests in containers to ensure consistent environments.
4. Use Caching and Artifacts
- 📦 Cache dependencies: Store dependencies locally to avoid re-downloading during each pipeline run.
- ♻️ Reuse build artifacts: Utilize artifacts from previous stages to save time and resources.
How to Choose a CI/CD Platform
Selecting the right CI/CD platform involves evaluating your team’s needs and the platform’s features. Here are key considerations:
1. Cloud-Based vs. Self-Hosted Options
- Cloud-based: Easy to set up and maintain, with infrastructure managed externally. Examples: GitHub Actions, CircleCI.
- Self-hosted: Provides more control and security for sensitive projects. Examples: Jenkins, TeamCity.
2. User-Friendliness
Choose a platform with:
- An intuitive UI.
- Clear and detailed documentation.
3. Integration with Tools and Languages
Ensure compatibility with:
- Your programming languages.
- Tools like source control systems, issue trackers, and cloud platforms.
4. Configuration Flexibility
Look for platforms offering:
- Script-based or UI-based pipeline configurations.
- Advanced customization for triggers and error handling.
5. Knowledge and Expertise
Consider your team’s familiarity with the platform. If experience is lacking:
- Opt for platforms with extensive documentation or tutorials.
- Evaluate the ease of onboarding and training.
Popular CI/CD Platforms
GitHub Actions
- Tight integration with GitHub.
- Ideal for projects stored on GitHub.
- Cloud-hosted, minimal setup required.
Jenkins
- Open-source, highly flexible.
- Suitable for self-hosted environments with specific requirements.
- Extensive plugin ecosystem.
JetBrains TeamCity
- Kotlin-based CI/CD configurations.
- Native support for multiple languages.
- Integrates well with Docker, Jira, and more.
CircleCI
- Quick setup with GitHub/Bitbucket.
- Offers both cloud and self-hosted options.
Azure DevOps
- Comprehensive toolset for cloud and on-premises deployments.
- Seamless integration with Azure services.
GitLab CI/CD
- Fully integrated with GitLab.
- Uses templates for rapid pipeline configuration.
Travis CI
- Simple setup with automated builds and notifications.
- Supports stages for dependent workers.
AWS CodePipeline
- Managed CI/CD service optimized for AWS.
- Automates builds, tests, and deployments.
Bitbucket Pipelines
- Native integration with Atlassian tools.
- Automated processes triggered by commits and pull requests.
Deciding on the Right CI/CD Platform
1. Scalability and Performance
- For high scalability: CircleCI, AWS CodePipeline.
- For cloud-specific needs: Azure DevOps.
2. Ease of Use and Learning Curve
- For user-friendly options: GitHub Actions, Travis CI.
3. Customization and Extensibility
- For complex workflows: Jenkins, TeamCity.
4. Cost Structure
- Free tier options: GitLab CI/CD, Bitbucket Pipelines.
- Usage-based pricing: Align with your budget and growth plans.
